Programming in C
John Samuel
CPE Lyon
Year: 2017-2018
Contact: john(dot)samuel(at)cpe(dot)fr







| Class | Dates |
|---|---|
| Class 1 | 12th September |
| Class 2 | 13th September |
| Class 3 | 19th September |
| Class 4 | 20th September |
| Class 5 | 26th September |
| Class 6 | 3rd October |

Note: No classes (Not an object-oriented programming
language!!!)


/* File: hello1.c
* prints message on the output screen.
* author: John Samuel
* This is a multiline comment
*/
#include
<stdio.h> // headers
// This is a
single-line comment
int main()
{
printf("Hello
World!!!");
return
0;
}
/* File: hello2.c
* prints message on the output screen
using a variable.
* author: John Samuel
* This
is a multiline comment
*/
#include <stdio.h> // headers
int main()
{
int year = 2017;
//variable declaration
printf("Hello World!!! This is year %d", year);
return 0;
}
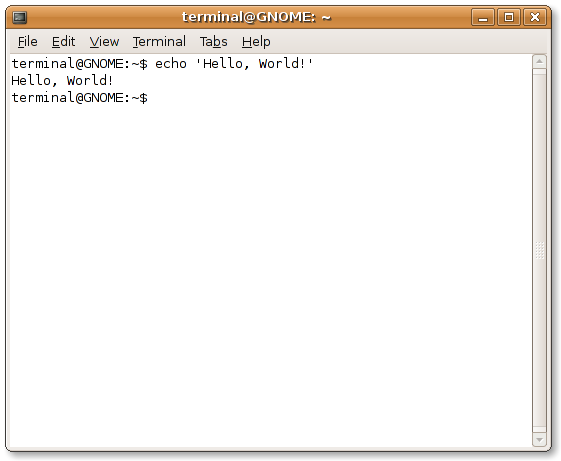
$ gcc hello1.c
$./a.out
Hello World!!!
$ gcc -o hello hello2.c
$./hello
Hello World!!! This is year 2017
// This is a single line comment
/* This is a multi-line
* comment
*/
| Data Type | C keyword | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| characters | char | 'h', 'a', ... |
| integers | short, int, long, long long | ...,-1,0,1,... |
| floating point numerals | float, double, long double | 3.14, 3.14e23 |
| enumeration | enum | STUDENT, INTERN |
| C keyword | Range |
|---|---|
| characters | signed char, unsigned char |
| integers | signed short, signed int, signed long, signed long long, unsigned short, unsigned int, unsigned long, unsigned long long |
Size limits of basic data types are machine-dependent!
char my_char_var = 'a';
Note: See the use of underscores in naming variables
char my_char_var = 'a';
unsigned char my_uchar_var = 234;
short my_short_var = -12;
unsigned short my_ushort_var = 65535;
int my_int_var = 12;
unsigned int my_uint_var = 3456;
long my_long_var = -1234553;
unsigned long my_ulong_var = 234556;
long long my_llong_var = 1123345;
unsigned long long my_ullong_var = 1234567;
float my_int_var = 3.14;
double my_uint_var = 3.14E-12;
long double my_long_var = 3.14E-22;
enum status {STUDENT, INTERN};
enum status s = STUDENT;
enum status {STUDENT=1, INTERN};
enum boolean {FALSE=0, TRUE};
Note: enum: unsigned int
| C keyword | Range |
|---|---|
| signed char | [SCHAR_MIN, SCHAR_MAX] |
| unsigned char | [UCHAR_MIN, UCHAR_MAX] |
| C keyword | Range |
|---|---|
| (signed) short int | [SHRT_MIN, SHRT_MAX] |
| unsigned short int | [0, USHRT_MAX] |
| (signed) int | [INT_MIN, INT_MAX] |
| unsigned int | [0, UINT_MAX] |
| (signed) long | [LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX] |
| unsigned long | [0, ULONG_MAX] |
| (signed) long long | [LLONG_MIN, LLONG_MAX] |
| unsigned long long | [0, ULLONG_MAX] |
| C keyword | Range |
|---|---|
| float | [FLT_MIN, FLT_MAX] |
| double | [DBL_MIN, DBL_MAX] |
| long double | [LDBL_MIN, LDBL_MAX] |
sizeof (char) //data type
sizeof (my_uchar_var) //variable
printf("%d",
my_int_var);
printf("%f",
my_float_var);
| C keyword | Format string |
|---|---|
| char | c |
| unsigned char | hhu |
| short | hd |
| unsigned short | hu |
| int | d, i |
| unsigned int | u |
| long int | ld |
| unsigned long int | lu |
| C keyword | Format string |
|---|---|
| long long int | lld |
| unsigned long long int | llu |
| float | f, F |
| double | g, G |
| long double | Lf |
| string of characters | s |
| Character | Format string |
|---|---|
| Newline | \n |
| Tab | \t |

int
value = 0b10100100;

int
value = 0b10100100;
printf("octal value: %o\n", value);


int
value = 0b10100100;
printf("hexadecimal value: %x\n", value);

| Operator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| + | addition |
| - | subtraction |
| * | multiplication |
| / | division |
| % | modulus operation |
int
a = 20,
b = 10;
| Operator | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| + | a + b | 30 |
| - | a - b | 10 |
| * | a * b | 200 |
| / | a / b | 2 |
| % | a % b | 0 |
| Operator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| < | less than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| > | greater than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| == | equal to |
| != | not equal to |
int
a = 20,
b = 10;
| Operator | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| < | a < b | 0 |
| <= | a <= b | 0 |
| > | a > b | 1 |
| >= | a >= b | 1 |
| == | a == b | 0 |
| != | a != b | 1 |
int
a = 20,
b = 0;
| Operator | Purpose | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| ! | Not | !a | 0 |
| && | And | a && b | 0 |
| || | Or | a || b | 1 |
int
a = 20,
b = 0;
| Operator | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| a++ | b = a++ | a = 21, b = 20 |
| ++a | b = ++a | a = 21, b = 21 |
| a-- | b = a-- | a = 19, b = 20 |
| --a | b = --a | a = 19, b = 19 |
int
a = 0x01000100;
| Operator | Purpose | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~ | NOT | ~a | 0xffffffbb |
| & | AND | a & 0x4 | 0x4 |
| | | OR | a | 0x2 | 0x46 |
| ^ | XOR | a ^ 0x4 | 0x40 |
| << | left shift | a << 1 | 0x88 |
| >> | right shift | a >> 1 | 0x22 |
int
a = 20,
b = 0;
| Operator | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | equal | a = b |
| += | addition assignment | a += b |
| -= | substraction assignment | a -= b |
| *= | multiplication assignment | a *= b |
| /= | division assignment | a /= b |
| %= | modulo assignment | a %= b |
Note: a op = b ::- a = a op b
| Operator | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| &= | bitwise AND assignment | a &= b |
| |= | bitwise OR assignment | a |= b |
| ^= | bitwise XOR assignment | a ^= b |
| <<= | bitwise left shift assignment | a <<= b |
| >>= | bitwise right shift assignment | a >>= b |
Note: a op = b ::- a = a op b
if (condition) {
...
}
int
a = 20,
b = 0;
if (a >
b) {
printf("a is greater than b");
}
if (condition1) {
...
} else if (condition2) {
...
} else {
...
}
Note: Non-zero values are considered true-value statements
Note: else is optional
int
a = 20,
b = 0;
if (a >
b) {
printf("a is greater than b");
} else if (a <
b) {
printf("a is less than b");
} else {
printf("a is equal to b");
}
Note: Non-zero values are considered true-value statements
switch (expression) {
case value1 : statements1
case value2 : statements2
...
default : statementsn
}
Note: expression must be one of char, short, int or long
int
a = 20;
switch (a) {
case 10 : statement1
break;
case 20 : statement2
case 30 : statement3
break;
...
default : statementn
}
Note: Both statement2 and statement3 will be executed.
if (1) {
printf("Hi");
} else {
printf("Hello");
}
for(initialization;condition;updation){
...
}
int
a = 0;
for( a = 0;
a > 10;
a++){
...
}
int
a = 0;
for(;
a > 10;
){
...
}
Note: Any or all of initialization, condition or updation statements can be missing.
int
a = 0;
for( a = 0;
a > 10;
a++){
...
a += 2 ;
...
}
while(condition){
...
}
int
a = 20;
while(a > 0){
...
a--;
...
}
int
a = 0;
while(a < 20){
...
a++;
...
}
do{
...
} while(condition);
int
a = 20;
do{
...
a --;
...
} while(a > 0);
int
a = 0;
do{
...
a ++;
...
} while(a < 20);
do{
...
if (condition1) {
...
break;
}
...
} while(condition);
do{
...
if (condition1) {
...
continue;
}
...
} while(condition);
while(condition){
...
if (condition1) {
...
break;
}
...
};
while(condition){
...
if (condition1) {
...
continue;
}
...
};
for(initialization;condition;updation){
...
if (condition1) {
...
break;
}
...
};
for(initialization;condition;updation){
...
if (condition1) {
...
continue;
}
...
};
are a collection of homogeneous elements

are rectangular arrays

are rectangular arrays

char name[20];
Note: C doesn't have a special data type called 'string'.
int iarray[20];
float farray[20];
double darray[20];
int i;
int array[20];
for ( i = 0;
i < 20; i++) {
array[i] =
i;
}
int prices[5] = {
11, 12, 13, 14, 15 };
int rooms[] = {
301, 302, 303 };
char message[] = "Hello World!!";
Note: We didn't specify size of rooms and message.
int prices[2][2] = {
{11, 12},
{13, 14}
};
int rooms[][] = {
{201, 202},
{301, 302}
};
char message[2][8] =
{"Hello", "World!!"};